Forensic Science Fundamentals and Investigations: An Overview
Forensic science, detailed in comprehensive handbooks, applies scientific principles to legal matters, offering crucial insights into criminal investigations and evidence analysis.
Key resources, like the FBI Handbook and Hall & Saferstein’s work, provide updated reviews of criminalistic practices and scientific testing methodologies for diverse evidence.
These volumes cover evaluation, interpretation, and application of tests, while newer editions incorporate the latest advancements in forensic laboratory procedures and practices.
Forensic science represents the application of diverse scientific disciplines to legal proceedings, fundamentally bridging the gap between scientific inquiry and the justice system. Comprehensive handbooks, such as those published by the FBI and authored by Hall & Saferstein, serve as foundational resources for understanding its core principles.
These texts detail how scientific methods are employed to analyze evidence collected from crime scenes, providing crucial insights for investigations. The field encompasses a broad spectrum of specialties, from criminalistics – the analysis of physical evidence – to specialized areas like DNA analysis and toxicology.
Modern forensic science isn’t static; it continually evolves with advancements in technology and scientific understanding. Updated editions of key handbooks reflect these changes, ensuring practitioners have access to the latest methodologies and interpretations. The goal remains consistent: to provide objective, reliable evidence to aid in the pursuit of justice, as outlined in detailed procedural guides.
Historical Development of Forensic Science
The roots of forensic science, though formalized later, trace back centuries, with early attempts to apply scientific reasoning to legal matters. However, the modern discipline truly began to take shape in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, driven by advancements in fields like chemistry, biology, and medicine.
Early pioneers focused on developing techniques for identifying poisons, analyzing bloodstains, and establishing personal identification methods – notably, fingerprinting. Landmark publications and the establishment of forensic laboratories, like those detailed in the FBI Handbook, marked significant milestones.
Over time, forensic science expanded its scope, incorporating new technologies like DNA analysis and digital forensics. Handbooks, continually updated since their original publication in 1982 (Pearson/Prentice-Hall), document this evolution, reflecting the increasing sophistication of investigative techniques and the growing reliance on scientific evidence in the courtroom.

The Role of the Forensic Scientist
Forensic scientists serve as crucial links between the scientific community and the legal system, applying their expertise to analyze evidence and provide objective findings in criminal investigations. Their responsibilities, as outlined in resources like the Forensic Science Handbook, encompass a wide range of tasks, from crime scene investigation to laboratory analysis and expert testimony.
These professionals meticulously examine physical evidence – be it trace materials, biological samples, or firearms – utilizing specialized techniques and adhering to strict protocols to ensure accuracy and reliability. The FBI Handbook emphasizes the Laboratory’s commitment to rigorous scientific standards.
Ultimately, the forensic scientist’s role is to present clear, unbiased interpretations of scientific data to assist in the pursuit of justice, contributing significantly to the comprehension and evaluation of evidence presented in legal proceedings.

Core Disciplines in Forensic Science
Forensic science encompasses criminalistics, biological and chemical analysis, and trace evidence examination, as detailed in comprehensive handbooks and FBI Laboratory resources.
Criminalistics: The Foundation
Criminalistics forms the bedrock of forensic science, meticulously applying scientific principles to legal investigations. As highlighted in various forensic handbooks, including those published by the FBI and Pearson/Prentice-Hall, this discipline focuses on the recognition, identification, individualization, and evaluation of physical evidence.
It encompasses a broad range of analyses, from examining firearms and ballistics to analyzing trace evidence like fibers and paint chips. These handbooks emphasize the importance of comprehending the application and interpretation of scientific tests performed on diverse evidence types.
Modern criminalistics, as described in updated editions, integrates advanced technologies and methodologies to enhance accuracy and reliability. The field’s core principles are essential for crime laboratories and related facilities, providing the foundation for sound forensic conclusions.
Biological Sciences in Forensics
Biological sciences play a pivotal role in modern forensic investigations, as detailed within comprehensive forensic science handbooks. These disciplines encompass a wide array of techniques, including DNA analysis, forensic entomology, and the examination of biological fluids and tissues.
DNA analysis, a cornerstone of forensic biology, allows for individual identification with remarkable accuracy, as explored in resources like the FBI Handbook. Forensic entomology utilizes insect life cycles to estimate time of death, offering crucial investigative leads.
The application of biological principles requires rigorous scientific methodology and adherence to strict quality control standards, as emphasized in updated editions of forensic texts. These techniques are vital for linking suspects to crime scenes and reconstructing events.
Chemical Analysis in Forensic Investigations
Chemical analysis forms a critical component of forensic science, providing essential data for reconstructing crime scenes and identifying unknown substances, as detailed in forensic handbooks. Techniques range from chromatography and spectroscopy to toxicology and arson investigation.
Toxicology, a key area, focuses on detecting and quantifying drugs and poisons in biological samples, aiding in determining cause of death or impairment. Arson investigation utilizes chemical analysis to identify accelerants and determine the origin of fires.
Forensic handbooks, including those from the FBI and Pearson/Prentice-Hall, emphasize the importance of validated methodologies and accurate interpretation of results. These analyses require specialized equipment and expertise to ensure reliable evidence presentation in legal proceedings.
Trace Evidence Analysis
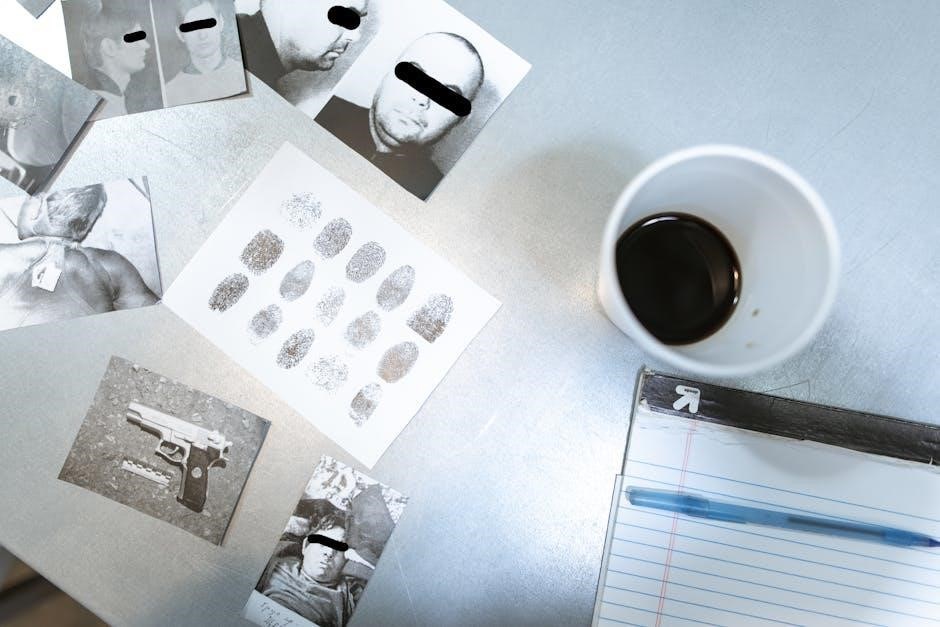
Trace evidence analysis, a cornerstone of forensic investigations, involves the examination of microscopic materials transferred during criminal activity, as outlined in comprehensive forensic science handbooks. This includes fibers, hair, paint chips, glass fragments, and gunshot residue.
Criminalistics, the foundation of forensic science, heavily relies on meticulous collection and analysis of these often-overlooked clues. Techniques like microscopy, spectroscopy, and chemical testing are employed to characterize and compare trace evidence.
Forensic handbooks, including those published by the FBI and Pearson/Prentice-Hall, detail the procedures for proper evidence handling and interpretation. Establishing a link between a suspect and a crime scene through trace evidence requires rigorous scientific methodology and careful documentation.

Forensic Investigation Procedures
Effective procedures, detailed in forensic handbooks, prioritize crime scene security, meticulous documentation, and maintaining a strict chain of custody for evidence integrity.
Crime Scene Investigation: Securing and Documenting
Initial response at a crime scene fundamentally involves securing the area, establishing a perimeter to prevent unauthorized access, and protecting potential evidence from contamination or alteration. Comprehensive documentation is paramount, utilizing detailed note-taking, sketches, and, crucially, forensic photography and videography.
Handbooks, such as those from the FBI and authored by Hall & Saferstein, emphasize the importance of a systematic approach to documentation, capturing the scene’s original state before any evidence is collected or moved. This includes recording the location of items, their condition, and any observable characteristics.
Proper documentation serves as a permanent record, vital for reconstructing the events and presenting findings in court. The meticulous nature of this phase directly impacts the integrity and admissibility of evidence, underpinning the entire forensic investigation process.
Evidence Collection and Preservation
Rigorous evidence collection is central to forensic investigations, demanding adherence to strict protocols to maintain integrity and prevent contamination. Forensic handbooks, including those by the FBI and Hall & Saferstein, detail proper techniques for collecting various types of evidence – from trace materials to biological samples.
Preservation methods are equally critical, varying based on the evidence type. This includes appropriate packaging, sealing, and storage conditions to prevent degradation or loss. Maintaining a detailed record of each item, its location, and the collection process is essential.
These procedures ensure the evidence remains legally admissible and scientifically reliable, forming the foundation for accurate analysis and ultimately, a just outcome in legal proceedings. Proper handling minimizes the risk of compromised results.
Chain of Custody: Maintaining Integrity
Maintaining a meticulous chain of custody is paramount in forensic science, ensuring the integrity and admissibility of evidence. Forensic handbooks, like the FBI’s and those authored by Hall & Saferstein, emphasize the importance of documenting every transfer of evidence.
This documentation includes the date, time, location, and the identities of individuals handling the evidence. Each person involved must sign and date the record, creating an unbroken timeline of possession.
Any break in this chain, or evidence of tampering, can render the evidence inadmissible in court, potentially jeopardizing a case. Strict adherence to chain of custody protocols is therefore a fundamental principle of forensic investigations, guaranteeing reliability.
Forensic Photography and Videography
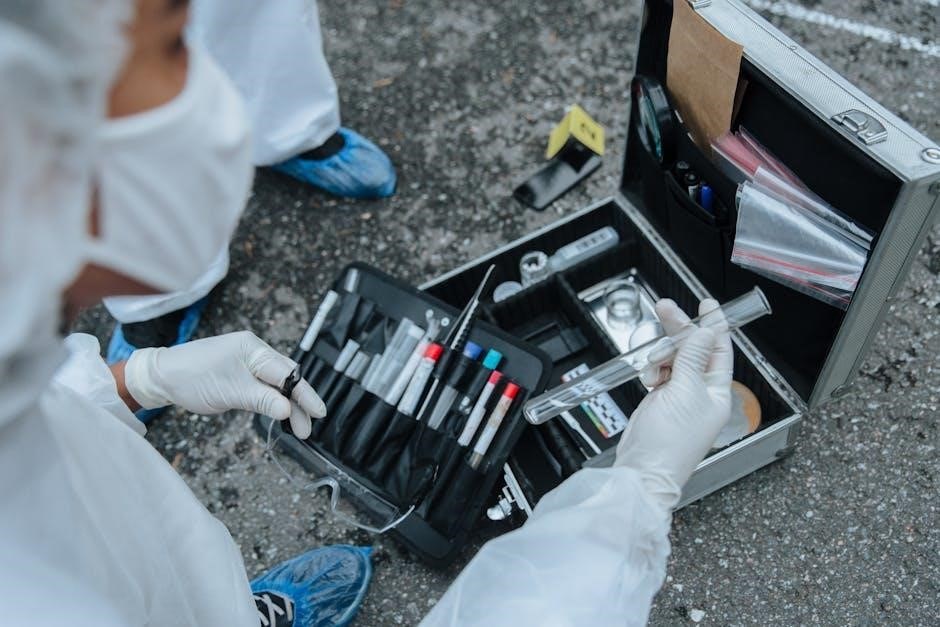

Forensic photography and videography are critical components of crime scene documentation, as detailed within comprehensive forensic science handbooks. These visual records provide an objective and permanent representation of the scene’s original condition.
Proper techniques involve capturing overall views, medium-range shots, and close-ups of evidence, utilizing scales for accurate size representation. Detailed notes accompany each image, documenting the date, time, location, and photographer’s identity.
Videography offers a dynamic perspective, allowing for a walkthrough of the scene. Both photography and videography, when properly executed and maintained within the chain of custody, serve as invaluable tools for investigation and courtroom presentation.

Specific Forensic Techniques
Forensic techniques, like DNA analysis, fingerprinting, ballistics, and toxicology, are thoroughly explored in forensic handbooks, aiding investigations and legal proceedings.
DNA Analysis: Principles and Applications
DNA analysis, a cornerstone of modern forensics, relies on identifying unique genetic markers within an individual’s DNA profile, as detailed in forensic science handbooks.
The process involves extracting DNA from biological evidence – blood, saliva, hair, or tissue – amplifying specific regions using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and then analyzing the resulting DNA fragments.
Forensic handbooks, including those from the FBI and authored by Hall & Saferstein, outline the principles of Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analysis, the current standard for DNA profiling.
Applications span from identifying suspects and victims to establishing familial relationships and exonerating the wrongly convicted, significantly impacting criminal justice.
These techniques, continually refined and updated, are essential for interpreting scientific tests on physical evidence, ensuring accuracy and reliability in legal contexts.
Modern advancements include analyzing degraded or limited DNA samples, expanding the scope of forensic investigations and enhancing investigative capabilities.
Fingerprint Analysis: Classification and Comparison
Fingerprint analysis, a long-established forensic technique, centers on the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on human fingertips, as detailed within forensic science handbooks.
The process involves classifying fingerprints into three primary patterns – loops, whorls, and arches – and identifying minutiae, or specific ridge characteristics, for comparison.
Forensic resources, like the FBI Handbook and works by Hall & Saferstein, outline methodologies for latent print development, lifting, and preservation at crime scenes.
Comparison is conducted by trained experts who analyze the location and orientation of minutiae in both known and unknown prints to determine a match.
This technique remains a powerful tool for identifying suspects, linking individuals to crime scenes, and providing crucial evidence in legal proceedings.
Modern advancements include automated fingerprint identification systems (AFIS) for database searching and enhanced visualization techniques for challenging prints.
Ballistics and Firearms Examination
Ballistics and firearms examination, a critical forensic discipline, focuses on analyzing firearms, ammunition, and the effects of projectiles, as detailed in forensic science handbooks.
The field encompasses internal ballistics (projectile’s motion within the firearm), external ballistics (projectile’s flight path), and terminal ballistics (projectile’s impact effects).
Forensic resources, including the FBI Handbook and texts by Hall & Saferstein, describe techniques for identifying firearms, matching bullets to specific weapons, and analyzing gunshot residue.
Examination involves comparing microscopic markings on bullets and cartridge cases to determine if they were fired from the same firearm, establishing a crucial link to a crime.
Trajectory analysis reconstructs the path of projectiles to determine the shooter’s location and the circumstances surrounding a shooting incident.
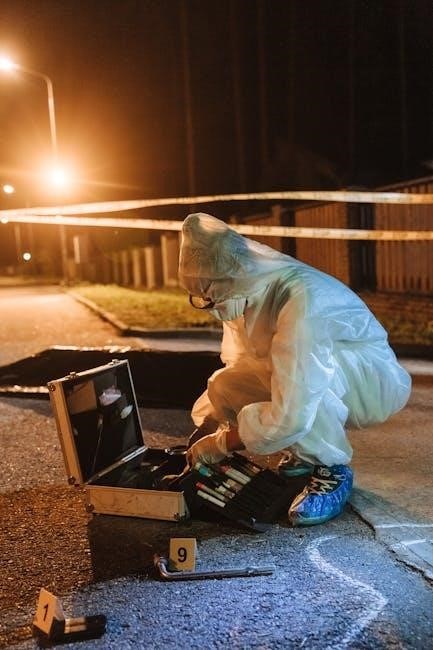

This discipline provides vital evidence in investigations involving shootings, armed robberies, and other firearm-related crimes.
Toxicology: Detecting Drugs and Poisons
Forensic toxicology, a vital component of forensic science, involves detecting and identifying drugs and poisons in biological samples, as outlined in comprehensive handbooks.
This discipline plays a crucial role in investigations involving drug-related deaths, poisoning, and impaired driving, providing critical evidence for legal proceedings.
Forensic resources, like the FBI Handbook and works by Hall & Saferstein, detail analytical techniques such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
Toxicologists analyze samples like blood, urine, and tissues to determine the presence and concentration of various substances, interpreting their effects on the body.
Analysis helps establish cause-of-death, assess impairment levels, and identify potential sources of poisoning, aiding law enforcement and medical examiners.
The field continually evolves with new drugs and toxins, requiring ongoing research and advancements in analytical methodologies.

Forensic Science Resources and Handbooks
Essential handbooks, including those from the FBI and authors Hall & Saferstein, offer updated reviews of criminalistics and scientific testing procedures.
The FBI Handbook of Forensic Science
The FBI Handbook of Forensic Science serves as a foundational resource, providing an introduction and comprehensive overview of the FBI Laboratory’s capabilities and commitment to rigorous scientific analysis.
This handbook details the application of scientific tests to a wide array of physical evidence encountered in criminal investigations, emphasizing the importance of accurate interpretation and evaluation.
It’s a valuable document for understanding the breadth of services offered by the Laboratory, covering various disciplines within forensic science, and highlighting the dedication to upholding the highest standards of quality and integrity.
Furthermore, the handbook reflects the evolving landscape of forensic science, incorporating advancements in techniques and methodologies used to analyze evidence and support legal proceedings, ensuring its relevance and utility.
Accessing this resource provides insight into the FBI’s role in advancing forensic science and its contribution to the pursuit of justice through scientific expertise.
Forensic Science Handbook (Hall & Saferstein)
The Forensic Science Handbook, authored by Adam B. Hall and Richard Saferstein, stands as a cornerstone text, fully updated and revised to reflect the latest developments in forensic testing and analysis.
This comprehensive resource delves into the scientific principles underpinning forensic investigations, covering a broad spectrum of subject areas relevant to crime laboratories and related facilities.
The handbook provides detailed insights into the interpretation of forensic evidence, equipping readers with the knowledge to comprehend and evaluate complex scientific data presented in legal contexts.
Its enduring value lies in its ability to bridge the gap between scientific theory and practical application, making it indispensable for students, practitioners, and anyone seeking a thorough understanding of forensic science.
Available in PDF and ePUB formats, this handbook remains a vital tool for navigating the intricacies of forensic science and its role in the justice system.
The Forensic Laboratory Handbook: Procedures and Practice
This essential handbook, a practical guide for forensic professionals, details the theories and practices currently employed in modern criminalistics, offering a wide-ranging overview of laboratory services.
Written by real-life practitioners, the book includes thirteen new chapters, ensuring readers benefit from expert insights and up-to-date methodologies in forensic science.
It meticulously describes the procedures and practices utilized in forensic laboratories, covering everything from evidence handling to complex analytical techniques.
The handbook’s strength lies in its focus on practical application, providing step-by-step guidance for conducting forensic examinations and interpreting results accurately.
A valuable resource for both seasoned professionals and those new to the field, it’s crucial for maintaining integrity and upholding the highest standards in forensic investigations.

Emerging Trends in Forensic Science
Modern forensics increasingly incorporates digital investigations into cybercrime, alongside forensic entomology utilizing insects, reflecting evolving scientific advancements and investigative techniques.
Digital Forensics: Investigating Cybercrime
Digital forensics, a rapidly expanding field within forensic science, focuses on the recovery and investigation of digital evidence found on devices like computers, smartphones, and storage media.
This discipline is crucial in cybercrime investigations, encompassing activities such as data extraction, analysis of network traffic, and identification of malicious software.
Forensic handbooks acknowledge the growing importance of digital evidence, detailing procedures for acquiring, preserving, and analyzing digital data while maintaining its integrity.
Investigators utilize specialized tools and techniques to uncover hidden files, recover deleted data, and trace the origins of cyberattacks, providing vital evidence for prosecution.
The FBI Handbook and other resources emphasize the need for skilled professionals capable of navigating the complexities of digital evidence and presenting findings in a legally sound manner.
As technology evolves, digital forensics continues to adapt, addressing new challenges posed by emerging cyber threats and ensuring the effective investigation of digital crimes.
Forensic Entomology: Utilizing Insects in Investigations
Forensic entomology represents a unique application of biological science within forensic investigations, focusing on the study of insects and their relation to criminal activity.
This field leverages the predictable life cycles and succession patterns of insects to estimate the post-mortem interval (PMI), or time elapsed since death, providing crucial information to investigators.
Forensic handbooks, while primarily focused on traditional forensic disciplines, increasingly recognize the value of entomological evidence in specific cases, particularly those involving decomposition.
Entomologists analyze insect colonization patterns on remains, considering factors like temperature, humidity, and geographic location to refine PMI estimations.
The presence, absence, and developmental stages of insects can also offer insights into whether a body has been moved or disturbed after death, aiding in reconstructing events.
As a specialized area, forensic entomology complements other forensic techniques, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of crime scenes and supporting legal proceedings.


























































































